-
×
 HI5005 - 5.00 pH@25°C - TQ - 500ml
1 × ฿1,658.50
HI5005 - 5.00 pH@25°C - TQ - 500ml
1 × ฿1,658.50 -
×
 BL931700-1 pH Mini Controller - 4 - 20mA output - 220V
1 × ฿15,515.00
BL931700-1 pH Mini Controller - 4 - 20mA output - 220V
1 × ฿15,515.00 -
×
 HI701 Checker HC ® - Free Chlorine
1 × ฿3,103.00
HI701 Checker HC ® - Free Chlorine
1 × ฿3,103.00 -
×
 HI93102 Water Analysis Meter (with Turbidity up to 50NTU)
1 × ฿64,200.00
HI93102 Water Analysis Meter (with Turbidity up to 50NTU)
1 × ฿64,200.00 -
×
 เครื่องวัดสีในน้ำตัวอย่าง HI727
1 × ฿3,103.00
เครื่องวัดสีในน้ำตัวอย่าง HI727
1 × ฿3,103.00 -
×
 น้ำยามาตรฐานสอบเทียบ
1 × ฿2,461.00
น้ำยามาตรฐานสอบเทียบ
1 × ฿2,461.00 -
×
 Reagents for HI 736 Checker HC ®, 25 Tests
1 × ฿535.00
Reagents for HI 736 Checker HC ®, 25 Tests
1 × ฿535.00 -
×
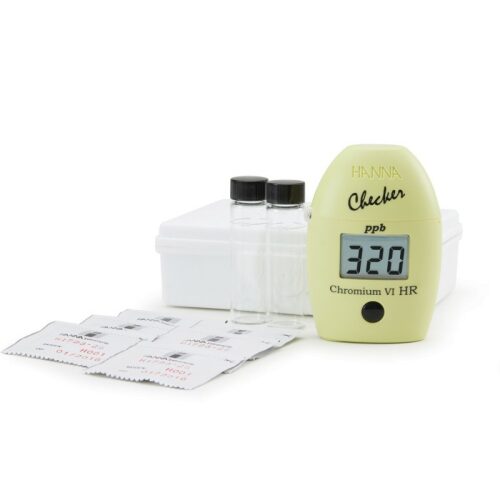 HI723 Checker HC ® - Chromium VI, HR
1 × ฿3,103.00
HI723 Checker HC ® - Chromium VI, HR
1 × ฿3,103.00 -
×
 เครื่องวัดปริมาณฟอสเฟต ช่วงต่ำสุด ในน้ำทะเล รุ่น HI774
1 × ฿3,103.00
เครื่องวัดปริมาณฟอสเฟต ช่วงต่ำสุด ในน้ำทะเล รุ่น HI774
1 × ฿3,103.00 -
×
 HI6007-01 - 7.010 pH@25°C - MQ - 1000ml
1 × ฿2,407.50
HI6007-01 - 7.010 pH@25°C - MQ - 1000ml
1 × ฿2,407.50 -
×
 HI3831T CTK Chlorine Total
1 × ฿1,337.50
HI3831T CTK Chlorine Total
1 × ฿1,337.50
Subtotal: ฿100,526.50