-
×
 เครื่องวัดปริมาณโครเมี่ยม ช่วงสูง รุ่น HI723
1 × ฿3,103.00
เครื่องวัดปริมาณโครเมี่ยม ช่วงสูง รุ่น HI723
1 × ฿3,103.00 -
×
 HI5013 - 13.00 pH@25°C - TQ - 500ml
3 × ฿1,658.50
HI5013 - 13.00 pH@25°C - TQ - 500ml
3 × ฿1,658.50 -
×
 HI93531 K-Type 1-Channel Handheld-Thermometer
1 × ฿11,770.00
HI93531 K-Type 1-Channel Handheld-Thermometer
1 × ฿11,770.00 -
×
 HI7091L - Reducing Pretreatment Solution, 500 ml
1 × ฿1,391.00
HI7091L - Reducing Pretreatment Solution, 500 ml
1 × ฿1,391.00 -
×
 pH/EC/°C Multiparameter Probe for HI 9811-5, HI 9812-5 & HI 9813-5
1 × ฿7,490.00
pH/EC/°C Multiparameter Probe for HI 9811-5, HI 9812-5 & HI 9813-5
1 × ฿7,490.00 -
×
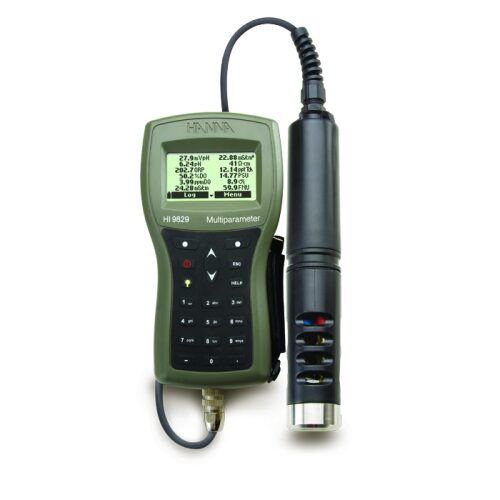 HI9829 Multiparameter pH/ISE/EC/DO/Turbidity Waterproof Meter with GPS option
1 × ฿225,128.00
HI9829 Multiparameter pH/ISE/EC/DO/Turbidity Waterproof Meter with GPS option
1 × ฿225,128.00 -
×
 HI3131B - Refillable Combination ORP Electrode for Titration and Laboratory Use
1 × ฿10,700.00
HI3131B - Refillable Combination ORP Electrode for Titration and Laboratory Use
1 × ฿10,700.00
Subtotal: ฿264,557.50