-
×
 HI766E2 K-Type, General Purpose w Cable
1 × ฿4,173.00
HI766E2 K-Type, General Purpose w Cable
1 × ฿4,173.00 -
×
 น้ำยามาตรฐานสอบเทียบ ค่ามาตรฐานความเค็ม
1 × ฿1,498.00
น้ำยามาตรฐานสอบเทียบ ค่ามาตรฐานความเค็ม
1 × ฿1,498.00 -
×
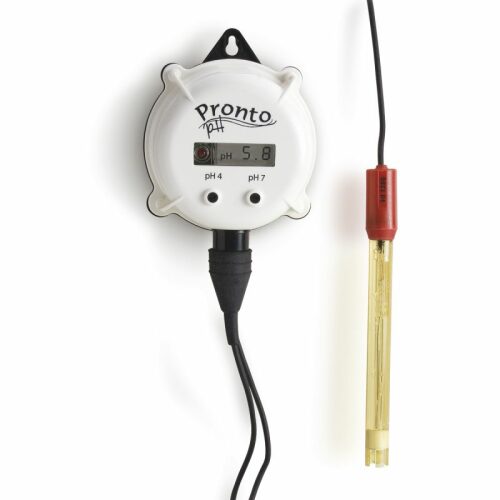 HI981402 pH-Indicator with LED-Alarm & Electrode PRONTO
1 × ฿0.00
HI981402 pH-Indicator with LED-Alarm & Electrode PRONTO
1 × ฿0.00 -
×
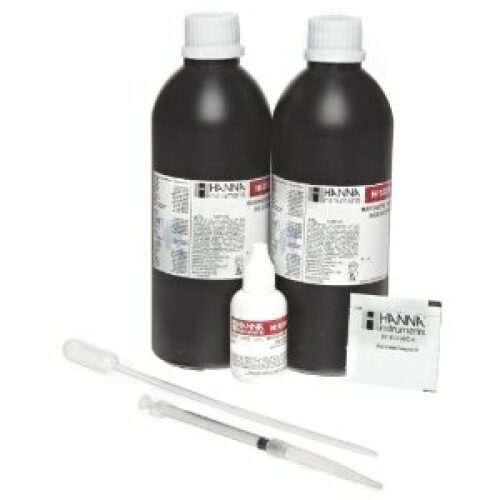 HI95747-01 Copper LR - Reagents - 100 Tests
1 × ฿6,955.00
HI95747-01 Copper LR - Reagents - 100 Tests
1 × ฿6,955.00 -
×
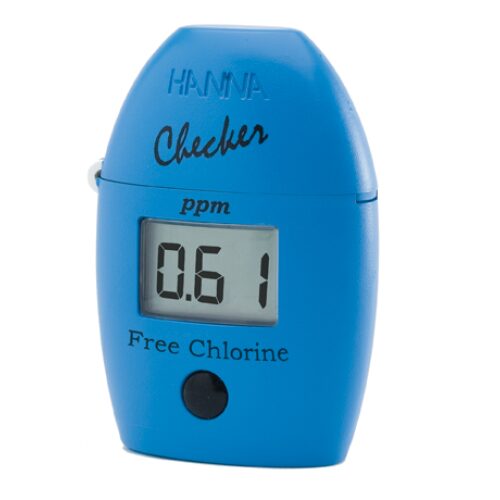 เครื่องวัดปริมาณคลอรีนอิสระ รุ่น HI701
1 × ฿3,103.00
เครื่องวัดปริมาณคลอรีนอิสระ รุ่น HI701
1 × ฿3,103.00 -
×
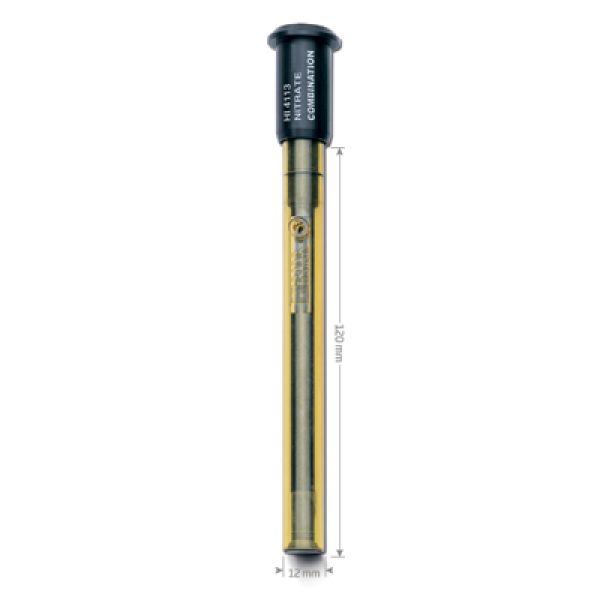 HI4113 - Nitrate ISE, Polymer membrane Combination
1 × ฿42,800.00
HI4113 - Nitrate ISE, Polymer membrane Combination
1 × ฿42,800.00 -
×
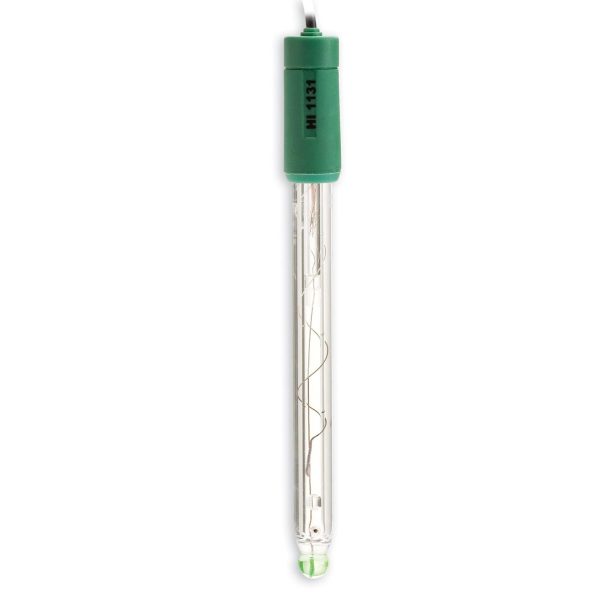 หัววัดค่ากรด-ด่าง แบบดิจิตอล รุ่น HI11311 พร้อม Matching pin ใช้งานสำหรับตัวอย่างทั่วไป
1 × ฿11,235.00
หัววัดค่ากรด-ด่าง แบบดิจิตอล รุ่น HI11311 พร้อม Matching pin ใช้งานสำหรับตัวอย่างทั่วไป
1 × ฿11,235.00 -
×
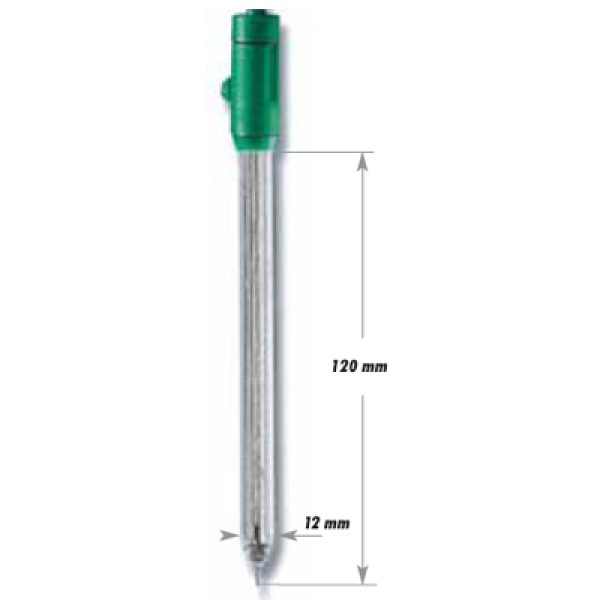 HI3618D - ORP/°C Electrode
1 × ฿11,235.00
HI3618D - ORP/°C Electrode
1 × ฿11,235.00 -
×
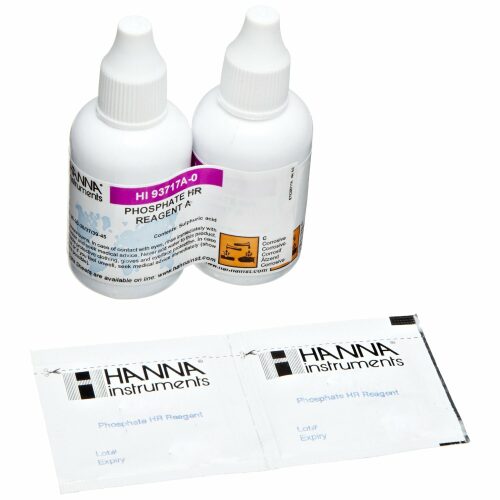 HI93717-01 Phosphate HR - Reagents - 100 Tests
1 × ฿1,658.50
HI93717-01 Phosphate HR - Reagents - 100 Tests
1 × ฿1,658.50 -
×
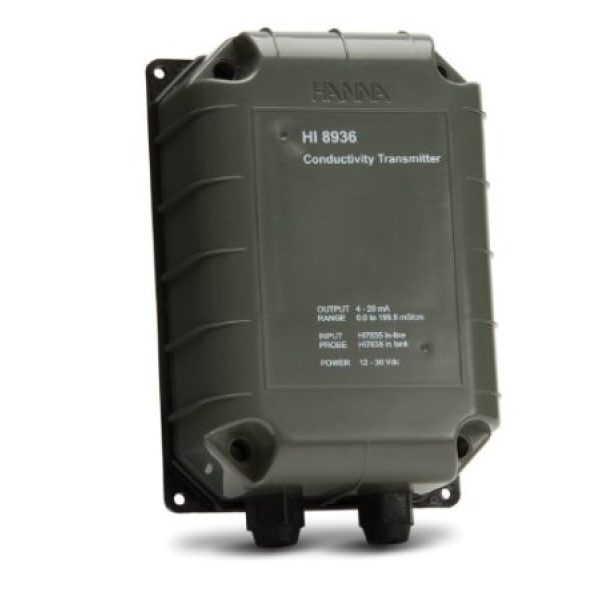 HI8936DN EC - Transmitter - 0.0 to 199.9 µS/cm
1 × ฿14,980.00
HI8936DN EC - Transmitter - 0.0 to 199.9 µS/cm
1 × ฿14,980.00 -
×
 Calibration Standard HI 721 Checker HC ®
1 × ฿802.50
Calibration Standard HI 721 Checker HC ®
1 × ฿802.50 -
×
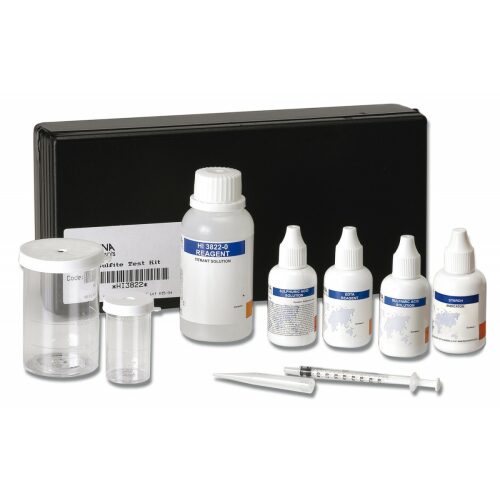 HI3822 CTK Sulfite
1 × ฿5,136.00
HI3822 CTK Sulfite
1 × ฿5,136.00
Subtotal: ฿103,576.00